Rabies
Rabies is an acute viral disease that causes fatal encephalomyelitis in virtually all warm-blooded animals including humans. The virus is found in the wild and some domestic animals and is transmitted to other animals and to humans through their saliva (following bites, scratches, and licks on broken skin and mucous membranes). In India, dogs are responsible for about 97% of human rabies, followed by cats (2%), and others (1%).
The disease is invariably fatal and perhaps the most painful and dreadful of all communicable diseases in which the sick person is tormented at the same time with thirst and fear of water (hydrophobia).
The burden of rabies in India
The global economic burden of rabies is estimated at US$ 8.6 billion from over 29 million people across the world receiving post-bite vaccinations annually. India is touted to have among the highest human rabies deaths in the world. India accounts for approximately 20,000 rabies-related human deaths each year out of the 59,000 global deaths. Fortunately, the development of rabies can be prevented to a large extent if animal bites are managed appropriately and in time. In this regard, the post-exposure treatment of animal bite cases is of prime importance. But lack of awareness about rabies and the prevalence of the fear of the series of post-bite injections are responsible for these unfortunate numbers.
97% of rabies deaths in India are caused by dog bites and 3% by bites or scratches from other mammals. Dogs are the main source of human rabies, up to 99% of all rabies transmissions to humans occur after dog bites.
According to a survey in 2008, the dog population in India was projected to be around 2.5 crores. In the past decade with rampant urbanization, changes in agriculture, and a stark rise in the amount of waste we generate, dog populations have risen.
National Rabies Control Programme
National Rabies Control Programme was approved during the 12th Five Year plan to control rabies in the country as a Central Sector Scheme under the umbrella of the National Health Mission (NHM) by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
The program had two components – Human and Animal Components.
The key strategic actions to achieve human health components are
- Ensure the availability of Anti Rabies Vaccine (ARV) and Anti Rabies Serum (ARS) to all animal bite victims.
- To encourage pre-exposure prophylaxis for High-Risk Groups
- To strengthen diagnostics capacity on rabies
- To promote operational research in the rabies
- Strengthening surveillance of animal bites and rabies cases in human
- Information, education, and communication (IEC) for increasing awareness about the diseases and the importance of seeking timely and appropriate treatment for animal bites
Animal health component - To achieve at least 70 % anti-rabies vaccination coverage among dogs in a defined geographical area annually for 3 consecutive years.
- Population survey of dogs
- Mass vaccination of dogs
- Dog population management
To accelerate the action towards the elimination of dog-mediated rabies by 2030 “National Action Plan for Dog Mediated Rabies Elimination from India by 2030” has been launched on World Rabies Day 2021.
National Action Plan for Dog-Mediated Rabies Elimination from India by 2030:
Vision: To achieve zero human deaths due to dog-mediated Rabies by 2030.
Mission: To progressively reduce and ultimately eliminate human rabies in India through sustained, mass dog vaccination and appropriate post-exposure treatment.
Key Principles of NAPRE:
The National Action Plan for Rabies Elimination (dog mediated) in India (NAPRE) is based on the following three key principles:
Prevention: Introduce cost-effective public health intervention techniques to improve accessibility, affordability, and availability of post-exposure prophylaxis to all people in need.
Promotion: Improve understanding of rabies through advocacy, awareness, education, and operational research.
Partnership: Provide coordinated support for the anti-rabies drive with the involvement of community, urban and rural civil society, government, private sectors, and international partners.
Though preventive measures like animal birth control programs and mass vaccination drives are being conducted by the government and NGOs for over a decade still the target of ‘zero by 30’ is far from us. Data play a huge role in designing future implementable actions. The data need to be accurate and is to be collected from the right source. A smart data collection and reporting system is the need of the hour.
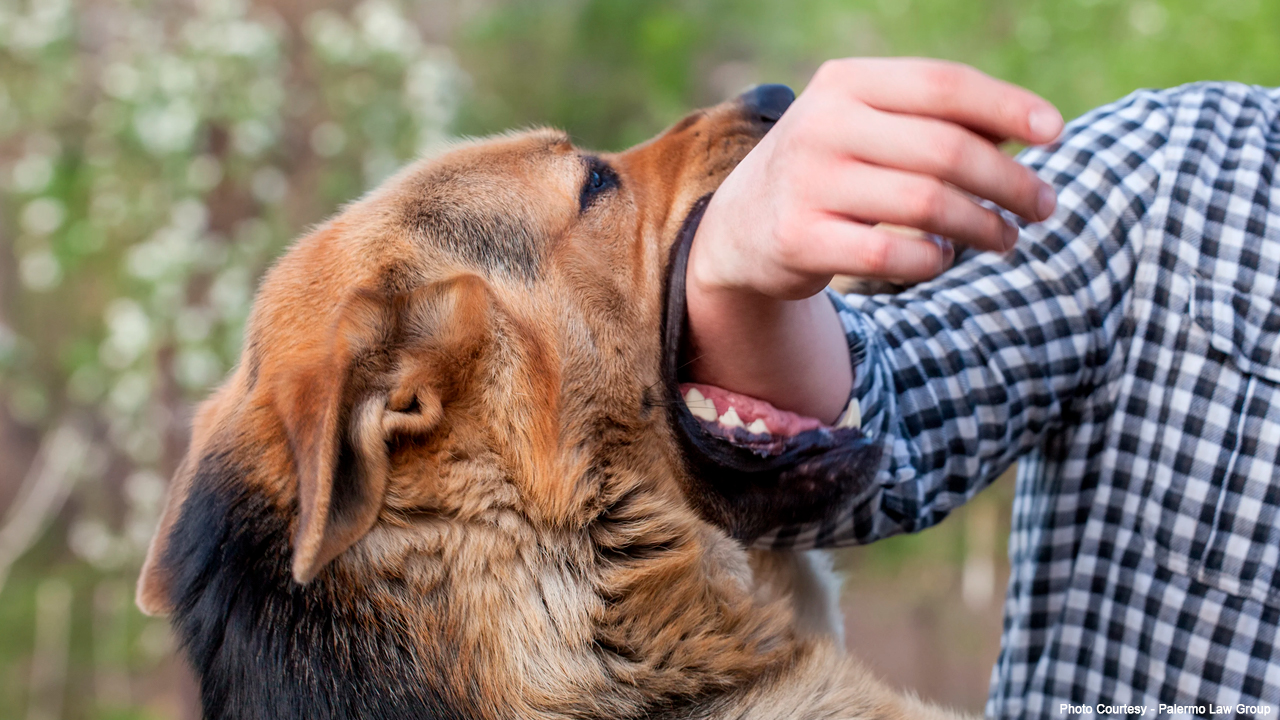

 Rabies is an acute viral disease and is transmitted from wild animals to humans through their saliva (following bites, scratches, and licks on broken skin and mucous membranes). Here’s all about the National Rabies Control Programme and NAPRE which comes under the umbrella of the National Health Mission (NHM).
Rabies is an acute viral disease and is transmitted from wild animals to humans through their saliva (following bites, scratches, and licks on broken skin and mucous membranes). Here’s all about the National Rabies Control Programme and NAPRE which comes under the umbrella of the National Health Mission (NHM).