Long-term exposure to air pollution appears to still be linked to higher mortality despite the existence of air quality standards that restrict levels of pollution, suggests a study published online in The BMJ today.
Researchers found evidence of higher death rates amongst people who had been exposed to more air pollution even though the levels were allowed under current official standards.
Previous studies have found an association between long term exposure to outdoor air pollution such as those in the form of fine particles in the air (known as particulate matter or PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and poor health or death.
Air pollution concentrations have fallen substantially in Europe since the 1990s, but it is unclear whether there still is a link between pollution and ill health or death at concentrations of pollution that are below current permitted limits.
Therefore, an international team of researchers led by the Institute for Risk Assessment Sciences at Utrecht University in the Netherlands set out to investigate if there was an association between low levels of air pollution concentrations and natural and cause-specific deaths.
Low level air pollution was defined as concentrations below current limit values as set by the European Union, US Environmental Protection Agency and the World Health Organization (WHO) air quality guidelines.
The researchers analysed data on eight groups of people within six European countries – Sweden, Denmark, France, the Netherlands, Germany and Austria – totalling 325,367 adults collectively.
Their study, known as the Effects of Low-Level Air Pollution: A Study in Europe (ELAPSE) recruited participants in the 1990s or 2000s.
Of the 325,367 participants who were followed up over an almost 20-year period, around 14.5% (47,131 people) died during the study period.
Analysis of the results showed that people who had higher exposure to particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide, and black carbon were more likely to die.
An increase of 5 µg/m3 (a concentration measure of particulate matter) in PM2.5 was associated with a 13% increase in natural deaths while the corresponding figure for a 10 µg/m3 increase in nitrogen dioxide was 8.6%. Associations with PM2.5 and nitrogen dioxide were largely independent of each other.
Moreover, associations with PM2.5, nitrogen dioxide, and black carbon remained significant at low to very low concentrations.
For people who were exposed to pollution levels below the US standard of 12 µg/m3, an increase of 5 µg/m3 in PM2.5 was associated with a 29.6% increase in natural deaths. People exposed to nitrogen dioxide at less than half the current EU standard of 40 µg/m3, a 10 µg/m3 increase in nitrogen dioxide was associated with a 9.9% increase in natural deaths.
This is an observational study, and as such, can’t establish cause.
The study also has some limitations, say the authors, such as the fact that it focused on exposure in 2010 which was towards the end of the follow-up period for most participants and, given the downward trend in air pollution, this measure might not exactly reflect the concentrations experienced during follow-up.
However, this was a large study from multiple European groups of people with the detailed information provided.
As such, the authors conclude: “Our study contributes to the evidence that outdoor air pollution is associated with mortality even at levels below the current European and North American standards and WHO guideline values.
“These findings are therefore an important contribution to the debate about the revision of air quality limits, guidelines and standards, and future assessments by the Global Burden of Disease [study].”
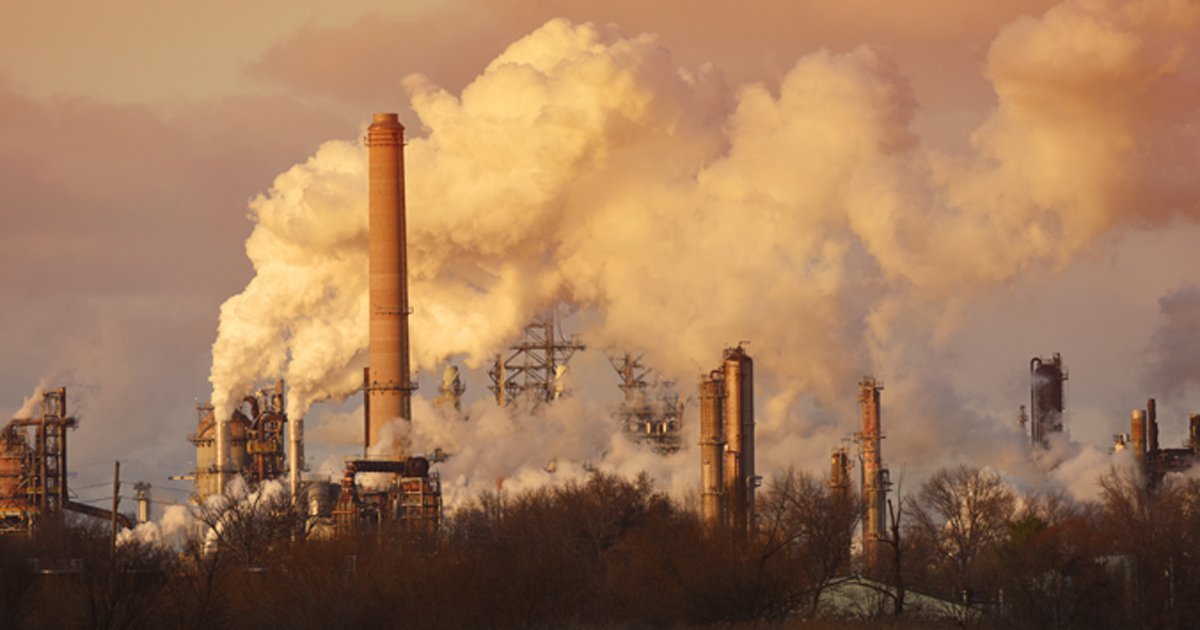

 Growing evidence that current pollution standards are insufficient and need to be revised, suggests the study
Growing evidence that current pollution standards are insufficient and need to be revised, suggests the study

















.jpg)















