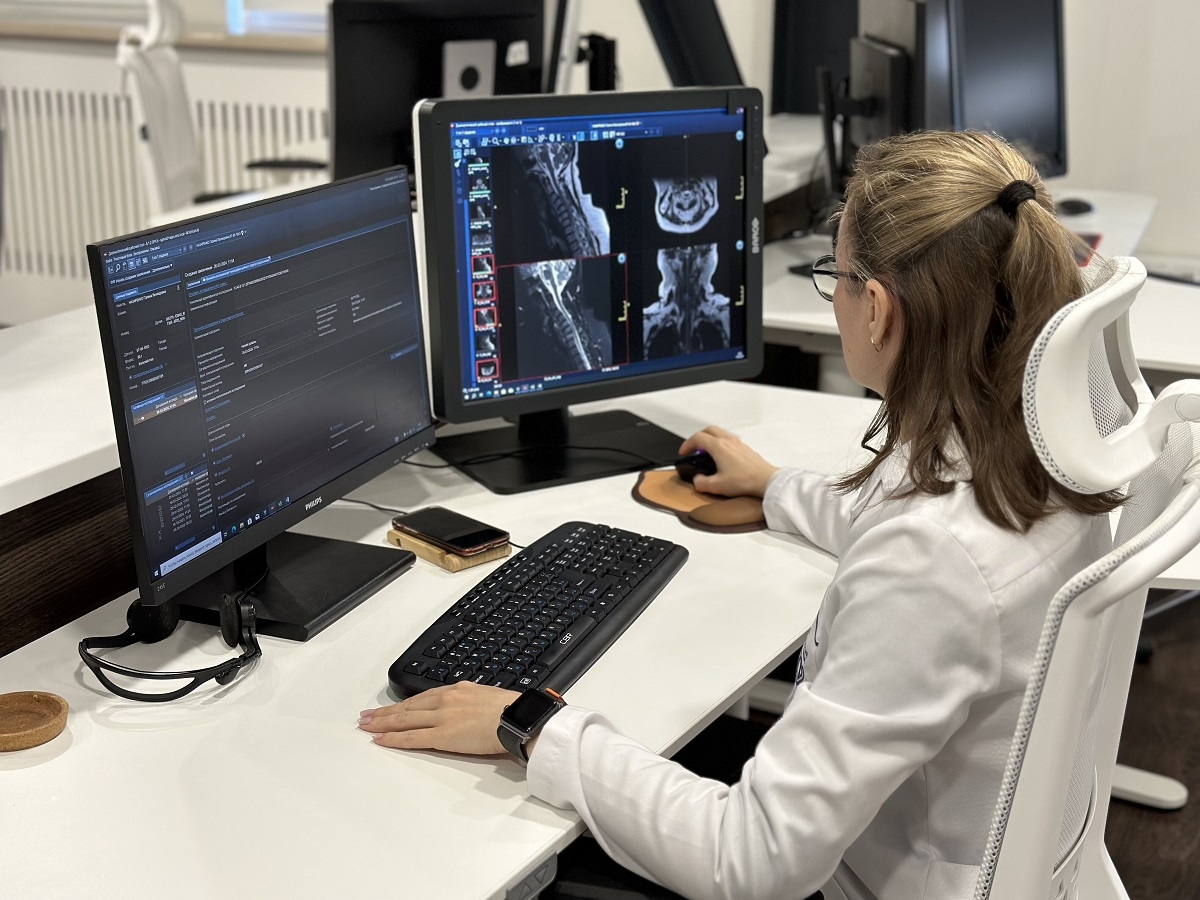
People with ‘silent’ COVID-19 infection have as much coronavirus in their noses and throats as those with symptoms, reveals research published online in the journal Thorax.
Given how many of these people there are---a fifth of those infected, the study findings show--they may have a key role in driving the spread of COVID-19, warn the researchers, who go on to suggest that this warrants extending testing provision.
People infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, but who don’t have symptoms, still carry the potentially transmissible virus, known as the viral load.
But just how large this viral load might be, and to what extent it might contribute to the spread of the virus, isn’t clear.
To try and find out, the researchers compared the viral load of 213 people, all of whom had tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, but not all of whom had symptoms of COVID-19 infection.
Following a large cluster outbreak of COVID-19 in Daegu City, South Korea, early on in the pandemic, the close contacts of this cluster (a religious group) were traced. This uncovered more than 3000 cases of COVID-19, ranging in symptom severity from none to severe.
Those with mild or no symptoms were admitted to dedicated care facilities for isolation and monitoring. The 213 participants in this study had been admitted to one such facility.
They were classified as symptomless if they had none of the following: fever; chills; muscle pain (myalgia); fatigue; runny nose (rhinorrhea); blocked nose; loss of taste or smell; sore throat; swallowing difficulties; cough; phlegm production; coughing up blood; headache; dizziness; loss of appetite; nausea; vomiting, abdominal pain; and diarrhoea.
Before the isolation period--an average of 6 days from the first swab test--around a fifth (41; 19%) people didn’t develop any symptoms: 39 (95%) of them had a further nose and throat swab test, 13 days, on average, after their initial diagnosis, to measure viral load.
Of the remaining 172 (81%) with mild symptoms, 144 were retested, adding up to a total of 183 who were included in the final analysis.
Over half of those without symptoms (21; 54%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, as did nearly two-thirds of those with mild symptoms (92; 64%). There was no significant difference in the viral load, however, between the two groups.
This is an observational study, and the researchers caution that positive swab test results don’t necessarily indicate the presence of the live virus.
Further studies are needed to clarify whether the persistence of viral DNA in people without any symptoms warrants precautionary quarantine measures, they say.
Most of the participants were also in their 20s and 30s so the findings might not apply to other age groups, they suggest.
Nevertheless, they point out: “Considering that most asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19 are likely to go unnoticed by healthcare workers and continue to reside within communities, such individuals may act as an essential driving force for the community spread of COVID-19 and the ongoing pandemic state.”
Until such time as it becomes clear how long, and to what extent, symptomless people might be infectious, testing should be extended to certain groups as a precautionary measure, recommend the researchers.
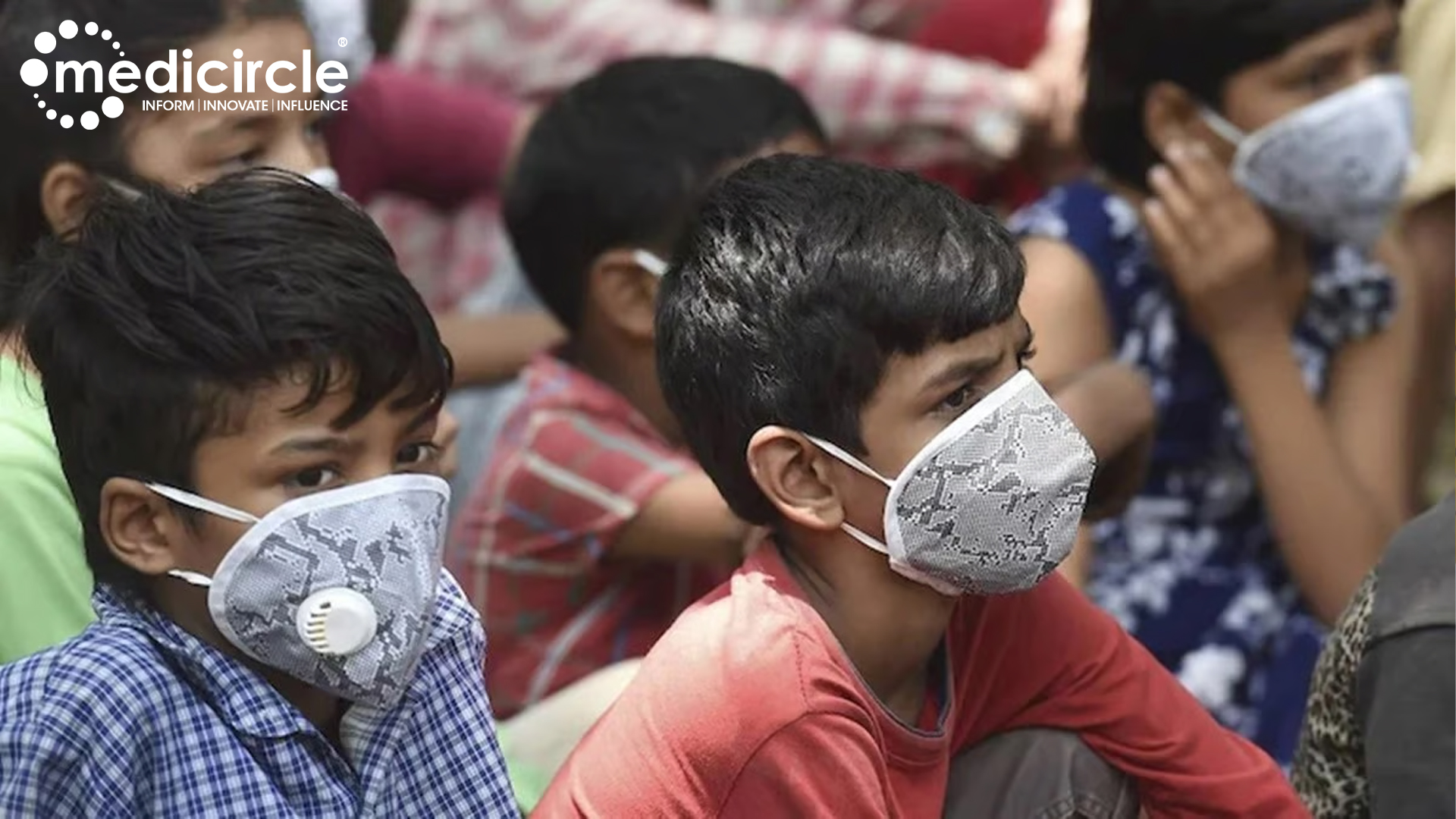
In a linked podcast, lead author Professor Sung-Han Kim explains: “Our data add further support to the general public use of face masks, regardless of the presence of symptoms, and suggest that the scope of SARS-CoV-2 testing should be expanded to include asymptomatic individuals in high-risk settings, such as nursing homes or healthcare facilities.”
 They are relatively common so may act as important driver of viral spread, warn researchers
They are relatively common so may act as important driver of viral spread, warn researchers