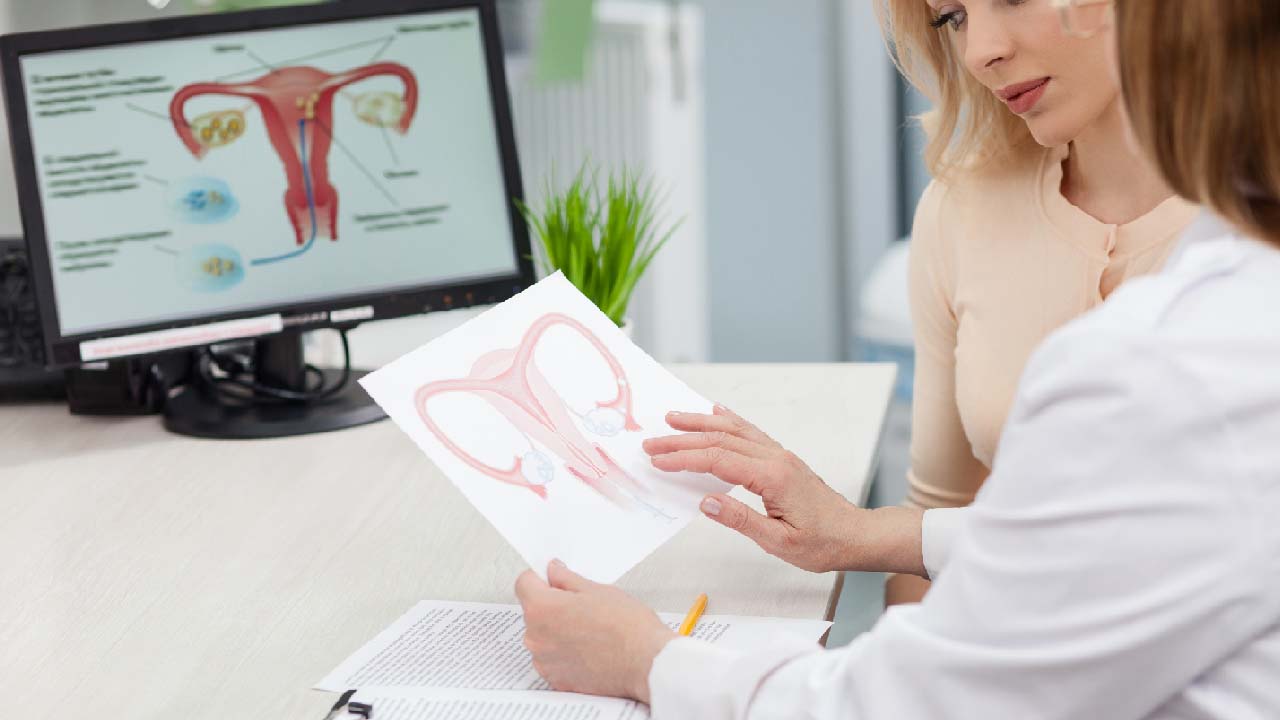
Cervical cancer begins in the cells that line the cervix, which is the lower portion of the uterus (womb). The cervix connects the uterus's body (where the fetus develops) and the vagina (birth canal). When cells in the body begin to grow out of control, cancer develops.
Most cervical cancers are caused by different strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. When the body is exposed to HPV, the immune system usually stops the virus from causing harm. However, in a small percentage of people, the virus can live for years, contributing to the transformation of some cervical cells into cancer cells. Cervical cancer can be avoided by having regular screenings and getting vaccinated against HPV infection.
Types of cervical cancer
Cervical cancers and pre-cancers are classified based on how they appear under a microscope in the lab. Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are the two most common types of cervical cancer.
- Squamous cell carcinomas make up the majority of cervical cancers (up to 9 out of 10). The cells of the exocervix give rise to these cancers. The transformation zone (where the exocervix meets the endocervix) is where most squamous cell carcinomas begin.
- Adenocarcinomas make up the majority of other cervical cancers. Cancers that arise from glandular cells are known as adenocarcinomas. The mucus-producing gland cells of the endocervix are the source of cervical adenocarcinoma.
- Cervical cancers, which are less common, have characteristics of both squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Adenosquamous carcinomas and mixed carcinomas are the terms for these types of cancer.
Although squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas account for the vast majority of cervical cancers, other cancers can arise in the cervix. Other types of cancer, such as melanoma, sarcoma, and lymphoma, are more commonly found in other parts of the body.
Early Warning Signs of Cervical Cancer
- Vaginal Bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Lower back pain
- Pain and swelling in the legs
- Unexplained weight loss
Factors Associated with Cervical Cancer
You may be more likely to develop cervical cancer if you:
- Have several sexual partners
- Take birth control pills for at least five years.
- Cigarette smoking
- Have a compromised immune system
- Have a sexually transmitted disease (STD)
The stages of cervical cancer
- Stage I: Cancer is found only in the cervix. It hasn't spread and is small.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread beyond your cervix and uterus but hasn't yet spread to your pelvic wall (the tissues that line the part of the body between hips) or vagina.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to the lower part of your vagina and may have spread to your pelvic wall, ureters (tubes that carry urine), and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to the bladder, rectum, or other parts of the body like bones or lungs.
HPV and cervical cancer
There are over 100 different types of HPV, and about a dozen of them have been linked to cancer. Early detection of these types of HPV is critical for cervical cancer prevention. Regular doctor-assisted screenings can help detect cell changes before they become cancerous. The HPV vaccine can help prevent HPV infection by protecting you against the HPV that causes up to 90% of all cervical cancers.
 Cervical cancer is often referred to as a "silent killer" because it often presents no symptoms in its early stages. Warning signs may appear as the disease progresses.
Cervical cancer is often referred to as a "silent killer" because it often presents no symptoms in its early stages. Warning signs may appear as the disease progresses. 










.jpeg)














.jpg)




