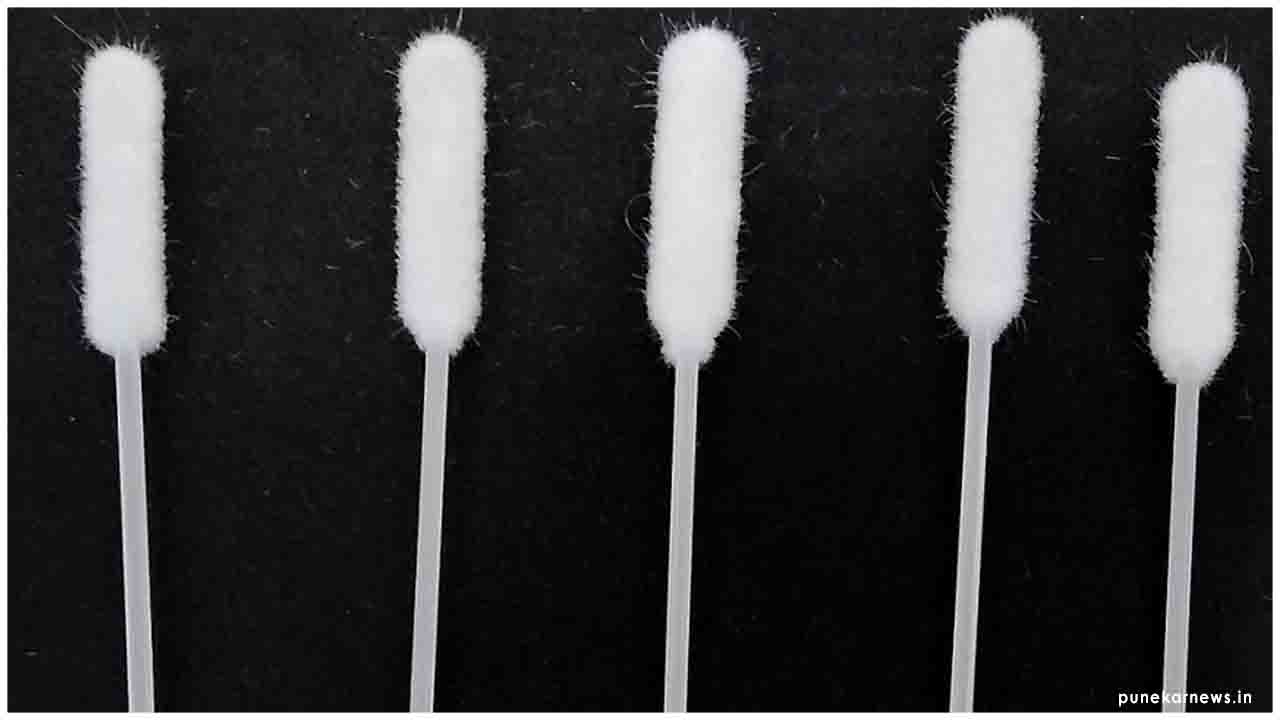
The National Chemical Laboratory (NCL) Pune has successfully developed an indigenous nasopharyngeal (NP) swab for collecting samples from the throat cavity of patients affected with Corona Virus which causes the Covid-19.
The NCL, a lab under the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), will manufacture one lakh nasopharyngeal swabs a day, a press release issued by the organisation said.A team of three scientists, Chandrashekhar V Rode, Dr Prakash P Wadgaonkar and Dr Anuya A Nisal worked on the specifications of nasopharyngeal swab polymers and adhesives.
The nasopharyngeal swab is a medical device with stringent specifications of quality, polymer grade, dimensions and sterilization. It consists of a cylindrical plastic stick with a brush-like tip of synthetic bristles/flocks.
Meanwhile,scientists at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), Guwahati, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, Govt of India, have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) based algorithms as an aid to rapid diagnosis and prediction of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
The framework developed by the research group at the Central Computational and Numerical Sciences Division, IASST led by Dr. Lipi B Mahanta, will also help grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
An indigenous dataset was developed by the scientists through collaborations to make for the unavailability of any benchmark oral cancer dataset for the study. Exploring different state-of-the-art AI techniques and playing with their proposed method, the scientists have gained unprecedented accuracy in oral cancer grading. The study was conducted applying two approaches through the application of transfer learning using a pre-trained deep convolutional neural network (CNN).
Four candidate pre-trained models, namely Alexnet, VGG-16, VGG-19, and Resnet-50, were chosen to find the most suitable model for the classification problem, and a proposed CNN model developed to fit the problem. Although the highest classification accuracy of 92.15% was achieved by the Resnet-50 model, the experimental findings highlight that the proposed CNN model outperformed the transfer learning approaches displaying accuracy of 97.5%. The work has been published in the journal Neural Networks.
As of now, the group is set for converting the algorithm into proper software to move on to carry out field trials. This is the next challenge that the group is prepared to meet, considering the ever-present gap between the health and IT sectors. Dr. Mahanta aspires for all the advanced infrastructural support to meet these challenges and feels that the software needs to be actively tested in hospitals, to make it truly robust, more accurate, and real-time worthy.
Around 16.1% of all cancers amongst men and 10.4% amongst women are oral cancer, and the picture is all the more alarming in NE India. Oral cavity cancers are also known to have a high recurrence rate compared to other cancers due to the high consumption of betel nut and tobacco.
This cancer group is characterized by epithelial squamous tissue differentiation and aggressive tumour growth, disrupting the basement membrane of the inner cheek region and thus can be graded by Broder’s histopathological system as well-differentiated SCC (WDSCC), moderately differentiated SCC (MDSCC) and poorly differentiated SCC (PDSCC). The cellular morphometry highlighting the tumour growth displays a very minute histological difference separating the three classes, which are very hard to capture by the human eye. It has remained elusive due to its highly similar histological features, which even pathologists find difficult to classify.
The advent of deep learning in AI holds an extraordinary prospect in digital image analysis to serve as a computational aid in the diagnosis of cancer, thus providing help in timely and effective prognosis and multi-modal treatment protocols for cancer patients and reducing the operational workload of pathologists while enhancing management of the disease.
 Innovations from NCL, Pune and IASST will go a long way in improving the healthcare and make it affordable
Innovations from NCL, Pune and IASST will go a long way in improving the healthcare and make it affordable



















.jpg)